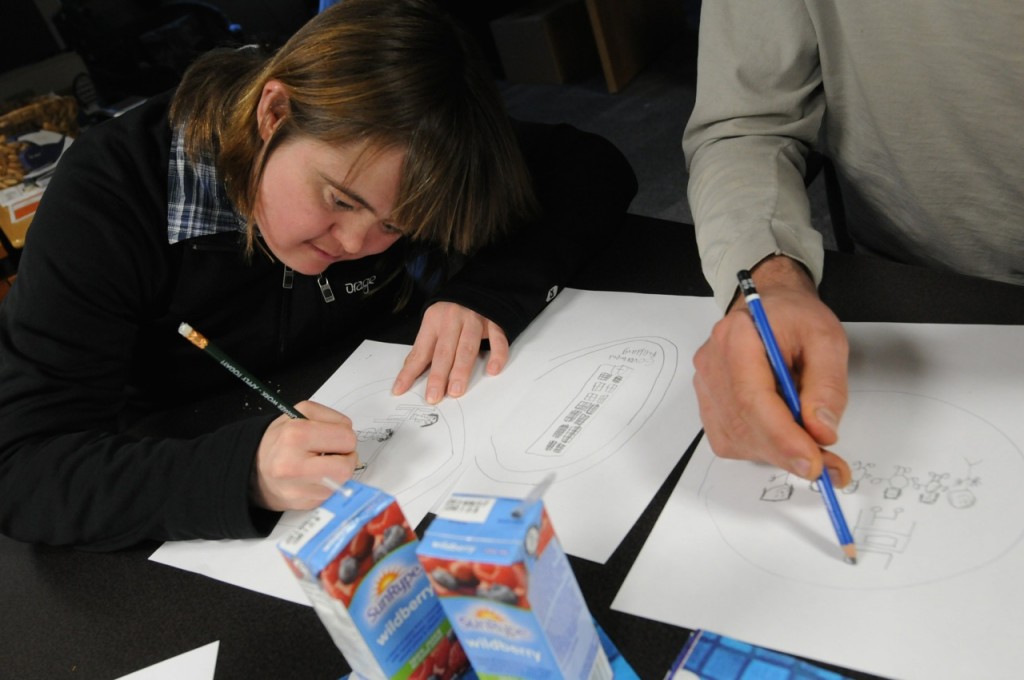
Participants were asked to draw pictures representing the five stakeholder groups. The drawings formed the basis for the icons used on the map markers. Photo courtesy the SpICE Lab (Spatial Information for Community Engagement)
By Naomi Bloch
In British Columbia, researchers have been using a crowdsourced mapping tool to capture positive employment experiences of individuals with intellectual disabilities. Geothink co-applicant Jon Corbett, an associate professor at the University of British Columbia’s Okanagan campus, is one of several UBC contributors to the participatory research project. Recently, the group published findings from its two-year pilot program.
The project is a collaboration between government agencies, the University of British Columbia, as well as self-advocates with intellectual disabilities and community partners. It demonstrates how government and citizens can employ the geoweb and participatory mapping to address community issues. “What we wanted to do specifically,” said Corbett, “was create a crowdsourced tool that would enable people to share their positive experiences, so that other people with intellectual disabilities and their family members and employers and also service providers could come to the site and they could actually see examples of positive employment. And so then they could emulate that, and they could strategize around that.”
This required developing an online environment that could engage all the identified stakeholder groups. To accomplish this, the initiative turned to the GeoLive participatory mapping tool, developed by Corbett’s Spatial Information for Community Engagement (SpICE) Lab. The GeoLive platform is a key component of a number of Geothink partner projects.
According to Corbett, GeoLive was initially conceived as a means to better support excluded and marginalized populations. “We know that when we share information on the cloud we have no idea how that information will be re-purposed, re-used, or stored,” Corbett said. “It can reappear in ways where we might least expect it in the future. So we wanted to get away from that and provide a certain level of guarantee that the information that people shared through the map is actually uniquely stored on our own servers, and should they wish to delete it they can delete it and it will be deleted forever.”
Corbett and GeoLive programmer Nick Blackwell are able to work directly with community members to customize the platform based on user needs. The software, which is built around the familiar Google Maps API, is now used both by community groups as well as academic researchers. In the process of working with their inclusive employment partners, Corbett and his colleagues gained new insights regarding some of the usability challenges on the participatory geoweb. These included spatial literacy issues, the need to make the platform more mobile-friendly and less reliant on keyboard interaction, as well as accommodating users who have limited familiarity with today’s social media conventions.
Self advocates with intellectual disabilities and other stakeholders collaborated with Corbett’s team to design, evaluate, and further customize the online mapping tool. The group then worked with individuals and organizations throughout the province to collect stories of successful and inclusive employment. Over eighty narratives are now included on the map. While some markers have simple text descriptions, others include video, audio, as well as photos.
The map now serves as a shared space for community engagement. At the same time, university researchers associated with the project have been able to analyze the collected stories to identify some of the common features described in participants’ positive employment experiences. Map contributors discuss issues such as the challenges of finding a job, as well as the social and practical factors that create an enriching work environment. These findings are expected to help inform best practice guidelines that can support employment services for people with intellectual disabilities in the future.
The map is now public, and anyone can contribute their own relevant experiences or explore other people’s stories at http://www.mappinginclusiveemployment.ca/.
Reference: Hole, R., Corbett, J., Cook, S., & de Raaf, S. (2015). Mapping inclusive employment practices for individuals with developmental disabilities: A participatory research mapping project. The BC Centre for Employment Excellence, 32 pages.
If you have thoughts or questions about this article, get in touch with Naomi Bloch, Geothink’s digital journalist, at naomi.bloch2@gmail.com.