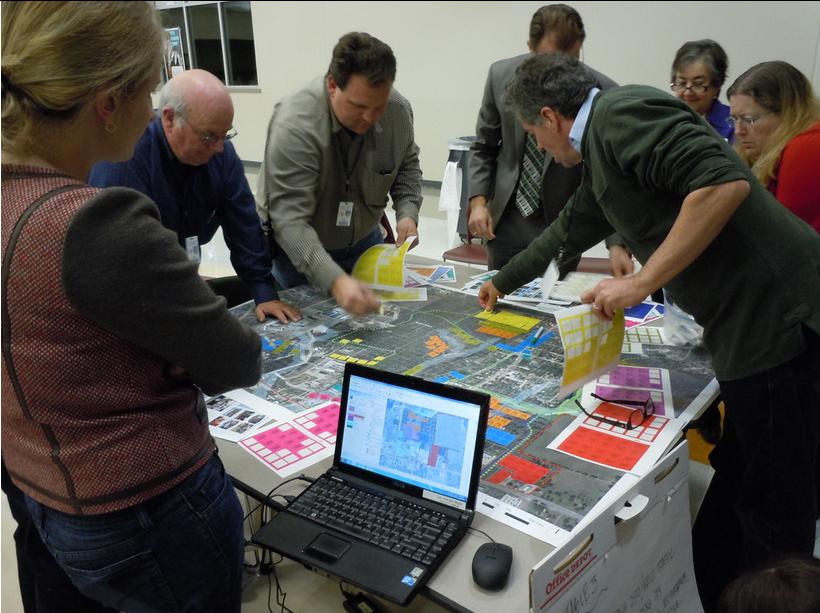
Robert Goodspeed, assistant professor of Urban Planning at the University of Michigan’s Taubman College of Architecture and Urban Planning, examined how decision support systems could be applied to urban planning processes during his doctoral work. This photo is of one such process in Dripping Springs, Texas.
By Drew Bush
The decision support market, a segment of the healthcare industry, made financial headlines when estimation of its global value by 2019 reached USD 239 billion, a jump of almost 38 billion since 2012. According to a new report, major players in the industry have poured money into new technologies that can take advantage of big data.
Digital health initiatives like those led by Canada Health Infoway have led to the creation of a network of systems that securely connect and share health information. Decision Support Systems like this one utilize computer-based data to aid in individual decision-making by supplying a massive bank of previous cases that aid in choosing the most likely answer or predicting trends. Most consist of interactive computer-based systems that utilize data and models to solve problems requiring geographically or temporally dispersed information.
In healthcare, IBM’s Watson system has been leading the trend to improve decisions made by doctors. “Watson knows what tests are relevant to further characterize a particular patient condition and what tests are not,” the report states. “It is a great help to physicians to have an assistant that is able to have read the latest journal articles and is loaded with medical information to recommend what tests may be relevant in a particular situation.”
An estimated 30 percent of all costs incurred for healthcare delivery come from tests that are either of little value in a patient’s case or sometimes outright wrong, according to some reports. Like platforms offered in other industries, the decision support system engineered by IBM offers the promise of more nuanced testing to enable better decisions on which medical tests can be best applied to specific patient conditions.

Robert Goodspeed, assistant professor of Urban Planning at the University of Michigan’s Taubman College of Architecture and Urban Planning, studies decision support systems.
Using decision support systems to analyze data and make better decisions has helped to improve processes in many industries. Geothink 2015 Summer Institute Instructor Robert Goodspeed, assistant professor of Urban Planning at the University of Michigan’s Taubman College of Architecture and Urban Planning, has studied this trend.
Although Goodspeed doesn’t work in healthcare, his research examines what he refers to as “planning support systems.” His work has looked at how we can use information technology to improve processes that engage community members in urban planning decisions. During his doctoral work, he created a process that allowed individuals to access information about their neighborhood and city to improve discussions.
This research involved community members placing stickers on maps to categorize specific areas for different land uses. This data was then transferred to digital form with one person entering the data as it was called out. Interactions such as this ensured entering the data could be reviewed by the group as a whole and reflected the ideas that they had discussed.
“The participants reported learning quite a bit and I could observe their plans evolving,” Goodspeed said. “So that’s just one example of the sorts of tools and practices that I think or feel we need. Especially as we’re facing issues like climate change where we want to quantify things and create indicators, and know how the plans we are creating are going to do or how they’ll perform against these different indicators.”
The Varied Uses of Decision/Planning Support Systems
In more recent research, Goodspeed has taken his work with planning support systems and applied it to improve environmental-decision-making processes surrounding North America’s Great Lakes ecosystems. Work he’s done as part of the Great Lakes Aquatic Habitat Framework project have used GIS datasets to examine aquatic habitats such as streams, rivers, and lakes in the region. The process also supplies a “big pile of data” for decision-makers in the fisheries and environmental management departments in Canada and the United States.
Unlike in planning where professional tasks follow a somewhat structured process, ecosystem-based management systems must consider a whole variety of information and tasks, Goodspeed said. Work in the project has included leading participatory design workshops for professionals north and south of the border to aid in the development of a tool that will one day allow easy digital examination off all the information on the Great Lakes collected for the project.
Community participation in planning processes that help to envision the possible future often result in a final product that’s inherently more understandable, Goodspeed added.
“And really it requires that kind of combination of creativity but being specific about what you think will happen and what you think will work,” he said of his work with decision-support systems. As big data is increasingly used to inform decision-making, this trend will only continue to grow beyond the industries of healthcare and environmental planning.
Tweet him @rgoodspeed.
If you have thoughts or questions about this article, get in touch with Drew Bush, Geothink’s digital journalist, at drew.bush@mail.mcgill.ca.